Fit¶
author: steeve laquitaine
Fit the standard Bayesian model to psychophysics circular estimates and use it make predictions.
Setup¶
[3]:
# go to the project's root path
import os
os.chdir("..")
[22]:
# import dependencies
from bsfit.nodes.models.bayes import StandardBayes
from bsfit.nodes.dataEng import (
simulate_dataset,
)
from bsfit.nodes.models.utils import (
get_data, get_data_stats, get_prediction_stats
)
from bsfit.nodes.viz.prediction import plot_mean
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from bsfit.nodes.cirpy.viz import plot_von_mises
import numpy as np
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
The autoreload extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext autoreload
Set parameters¶
[9]:
# set the parameters
SUBJECT = "sub01"
PRIOR_SHAPE = "vonMisesPrior"
PRIOR_MODE = 225
OBJ_FUN = "maxLLH"
READOUT = "map"
PRIOR_NOISE = [80, 40] # e.g., prior's std
STIM_NOISE = [0.33, 0.66, 1.0]
INIT_P = {
"k_llh": [2.7, 10.7, 33],
"k_prior": [2.7, 33],
"prior_tail": [0],
"p_rand": [0],
"k_m": [2000],
}
CENTERING = True
Simulate dataset¶
[10]:
# simulate a training dataset
train_dataset = simulate_dataset(
stim_noise=STIM_NOISE,
prior_mode=PRIOR_MODE,
prior_noise=PRIOR_NOISE,
prior_shape=PRIOR_SHAPE,
)
# use the train dataset as test to show
# best predictions
test_dataset = get_data(train_dataset)
Train model and predict¶
[11]:
# instantiate the model
model = StandardBayes(
initial_params=INIT_P,
prior_shape=PRIOR_SHAPE,
prior_mode=PRIOR_MODE,
readout=READOUT
)
# train the model
model = model.fit(dataset=train_dataset)
Training the model ...
-logl:50265.93, aic:100549.87, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:63349.73, aic:126717.45, kl:[ 2.835 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:50284.86, aic:100587.73, kl:[ 2.7 11.235 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:64023.04, aic:128064.09, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 34.65], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:67066.68, aic:134151.37, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.835 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:69232.46, aic:138482.91, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 34.65], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:50265.93, aic:100549.87, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.05], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:50265.93, aic:100549.87, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:3871.50, aic:7761.00, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
-logl:50265.93, aic:100549.87, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2100.00
Warning: Maximum number of function evaluations has been exceeded.
Training is complete !
The fitted model’s attributes are:
[12]:
# list the model's attributes
model.get_attributes()
[12]:
['prior_shape', 'prior_mode', 'readout', 'best_fit_p', 'neglogl', 'params']
The model’s fixed parameters are:
[13]:
# look at the model ...
model.params["model"]["fixed_params"]
[13]:
{'prior_shape': 'vonMisesPrior', 'prior_mode': 225, 'readout': 'map'}
The model’s learnt parameters are:
[14]:
# and at ... its best fit parameters
model.best_fit_p.tolist()
[14]:
[2.7, 10.7, 33.0, 2.7, 33.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.00025, 2000.0]
[16]:
# get predictions
output = model.predict(test_dataset, granularity="mean")
print("predictions data:", list(output.keys()))
Calculating predictions ...
-logl:3871.50, aic:7761.00, kl:[ 2.7 10.7 33. ], kp:[ 2.7 33. ], kc:[1.], pt:0.00, pr:0.00, km:2000.00
predictions data: ['PestimateGivenModel', 'map', 'conditions', 'prediction_mean', 'prediction_std']
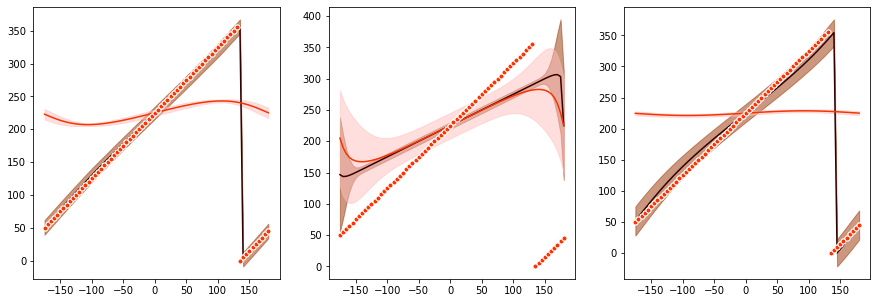
Plot stats for data & predictions¶
We calculate the data and prediction mean and standard deviations.
[17]:
# get data stats
estimate = test_dataset[1]
output = get_data_stats(estimate, output)
# get prediction stats
output = get_prediction_stats(output)
We plot the stats.
[18]:
# plot
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
plot_mean(
output["data_mean"],
output["data_std"],
output["prediction_mean"],
output["prediction_std"],
output["conditions"],
prior_mode=PRIOR_MODE,
centering=CENTERING,
)
Look at the model’s trained parameters¶
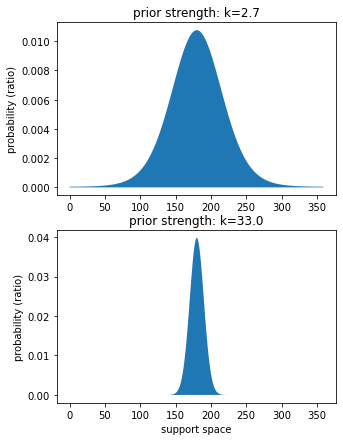
Measure the strengths of the priors¶
[38]:
# set support space and get strength
prior_strengths = model.best_fit_p.tolist()[3:5]
support_space = np.arange(0,360,1)
n_strengths = len(prior_strengths)
plt.figure(figsize=(5,7))
for ix, k_p in enumerate(prior_strengths):
# set panel
plt.subplot(n_strengths,1,ix+1)
# plot prior
plot_von_mises(support_space, k_p)
# legend
plt.title(f"prior strength: k={k_p}")
plt.ylabel("probability (ratio)")
if ix == len(prior_strengths)-1:
plt.xlabel("support space")
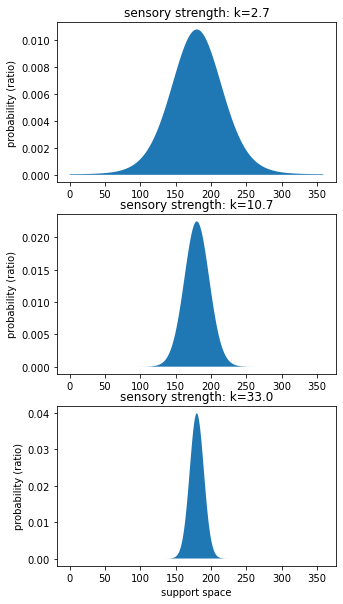
Measure the strengths of the sensory stimulus (llh)¶
[39]:
# get strength
sensory_strength = model.best_fit_p.tolist()[0:3]
n_strengths = len(sensory_strength)
plt.figure(figsize=(5,10))
for ix, k_s in enumerate(sensory_strength):
# set panel
plt.subplot(n_strengths,1,ix+1)
# plot prior
plot_von_mises(support_space, k_s)
# legend
plt.title(f"sensory strength: k={k_s}")
plt.ylabel("probability (ratio)")
if ix == len(sensory_strength)-1:
plt.xlabel("support space")
Measure motor noise¶
[42]:
# plot prior
k_m = model.best_fit_p.tolist()[8]
plot_von_mises(support_space, k_m);
plt.title(f"motor noise: k={k_m}");
plt.ylabel("probability (ratio)");
plt.xlabel("support space");

Tutorial complete !